Negative Testing: What, Why, and How?
Published on: May 19, 2025
Writing about a basic yet essential concept in software testing today — Negative Test Cases. The title already gives away the idea: Negative test cases are those designed to test the system's behavior when it receives invalid, unexpected, or incorrect inputs. These are the scenarios that a user shouldn't follow — but we still need to test them because users make mistakes, systems interact unpredictably, and vulnerabilities often hide in edge cases.
Understanding Through a Simple Example
Let’s take a common example: testing a login page.
In positive testing, the system is verified for correct behavior when a user enters a valid username and password. The expected result is a successful login and redirection to the dashboard or homepage.
Now comes negative testing. This involves checking how the system handles:
- Wrong username
- Wrong password
- Blank fields
- Special characters or script injections
- Inputs exceeding character limits
The goal is to ensure the application:
- Denies login with incorrect credentials
- Displays appropriate error messages
- Handles input gracefully (no crashes or erratic behavior)
- Prevents security risks such as SQL injection
Going Beyond the Basics
While login pages are simple examples, negative testing is vital across all testing layers. Here are a few advanced use cases:
1. API Testing
Sending malformed JSON or incorrect data types to an endpoint should return a proper error (e.g., 400 Bad Request) and not crash the service.
2. Form Validation
Examples include:
- Missing required fields
- Incorrect date formats
- Entering numbers where text is expected
- Invalid cross-field dependencies (e.g., end date before start date)
3. Database-Level Testing
Testing for violations of:
- Unique constraints
- Foreign key relationships
- Null constraints
4. Security-Focused Testing
Includes attempts such as:
- Bypassing authentication
- Accessing unauthorized content
- Injecting SQL or scripts
Why Negative Testing Matters
Negative test cases help:
- Uncover hidden bugs
- Validate error handling and fallback processes
- Prevent application crashes
- Strengthen data validation and input restrictions
- Improve user experience with meaningful feedback
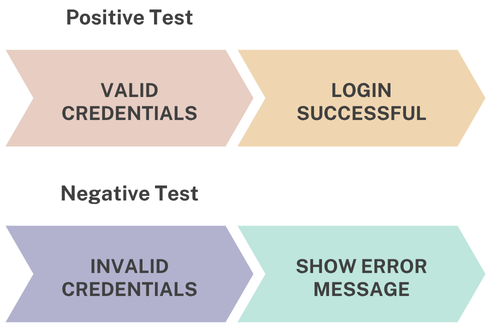
Positive vs Negative Testing
This visual can be extended further using tools like draw.io or Canva by adding various negative test scenarios such as blank fields, special character inputs, etc.
Final Thoughts
While positive test cases confirm that the application performs as intended, negative test cases ensure it doesn't do what it shouldn't. Both are essential, but negative testing often reveals the real-world issues that cause systems to break. A robust testing strategy is never complete without them.